If an FTP site is open on the Internet and private data is involved (e.g., backup photos), it needs to be encrypted during transmission.
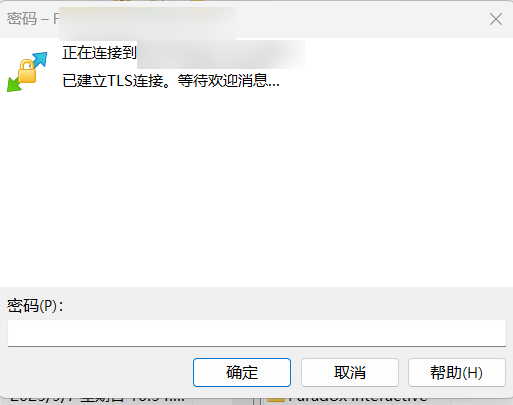
FTP built with IIS supports FTPS and can be set to either allow SSL or require SSL to provide compatibility.Windows Explorer does not support FTPS, so when using Explorer to access a site with FTPS, it will automatically switch to normal FTP without encryption if it is set to allow SSL mode.
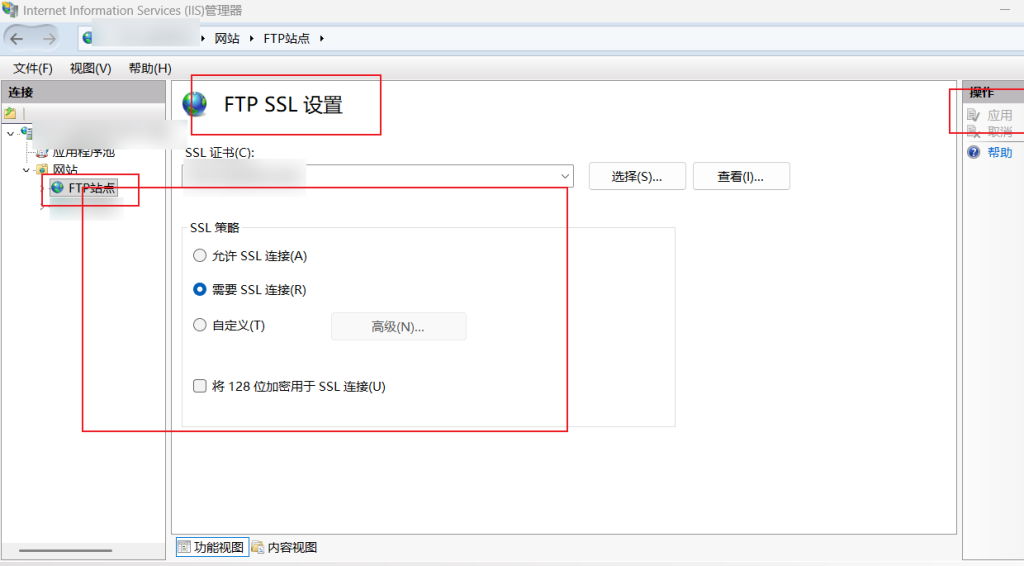
After setting up FTP, first check the main IIS server, which will have the option [FTP SSL Settings].
Check the configured certificates and check [Require] if full encryption is required, or [Allow] for compatibility or convenience. However, sometimes transfers are not encrypted (e.g. using Windows Explorer to access an FTP (FTPS) site).
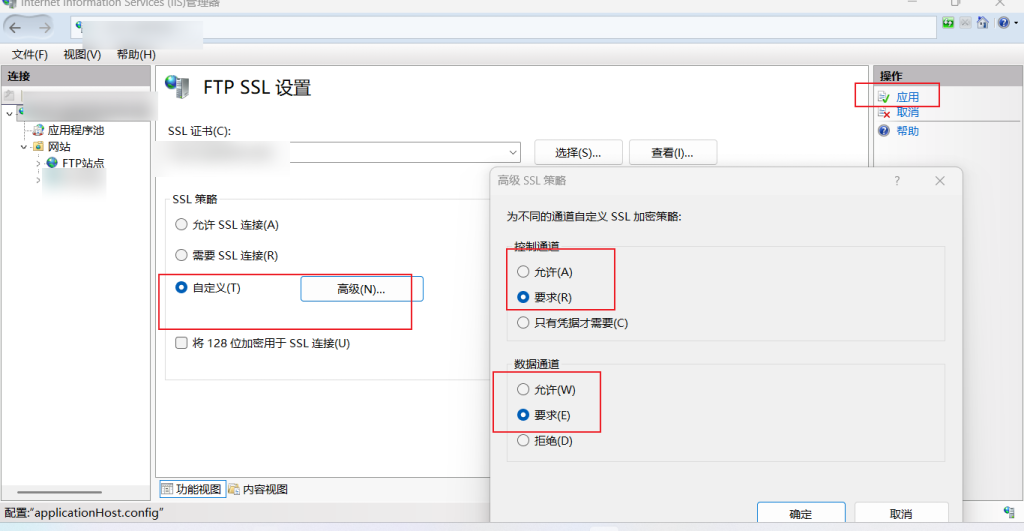
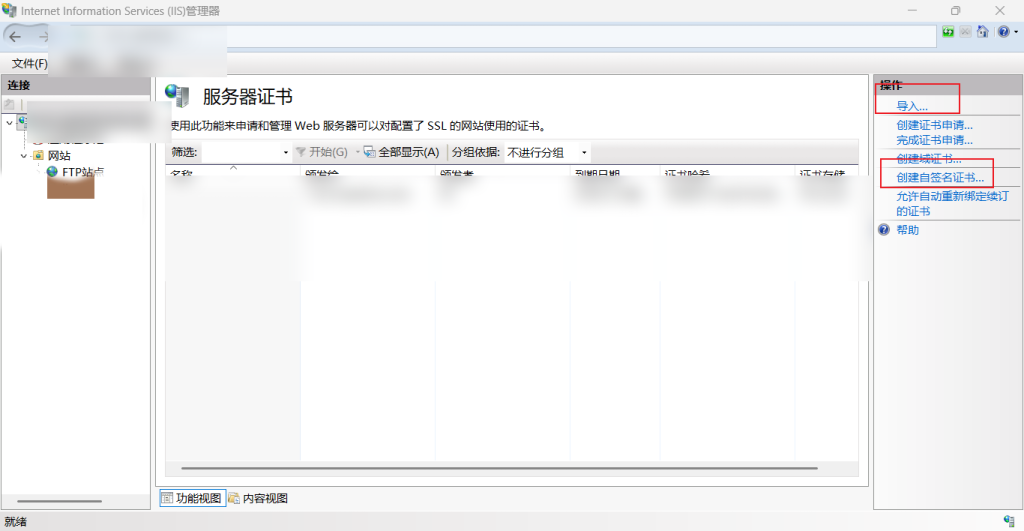
If you don't have an official certificate, you can create a self-signed certificate for testing, but it is recommended that you use a certificate from a trusted CA in a public network environment, otherwise a certificate warning will appear on the client.
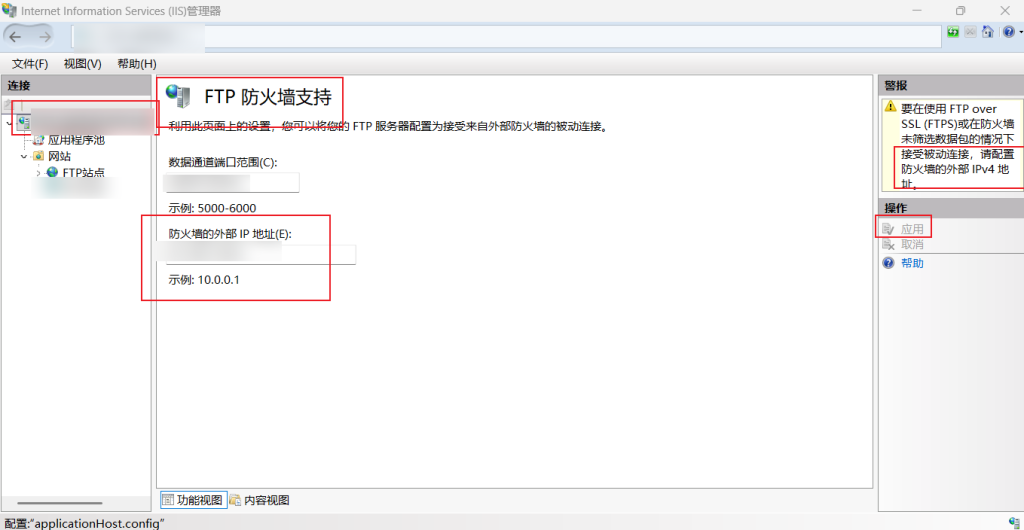
In addition, when using port mapping such as FRP, theIf you do not configure an "external IP address" in IIS, the server will return an internal address (e.g. 127.0.0.1 or an internal LAN address) in the PASV responseThis will result in the client not being able to establish a data connection. Therefore, you must set [external IP address of firewall] so that IIS advertises the correct public address to clients in passive mode.
Once configured, the same SSL configuration is performed for the individual FTP sites, and the FTPS site is finally accessible.